Magnesium, zinc, and aluminum are the most commonly used metals in high-pressure die casting due to their favorable properties such as lightweight, mechanical strength, and surface finish quality.
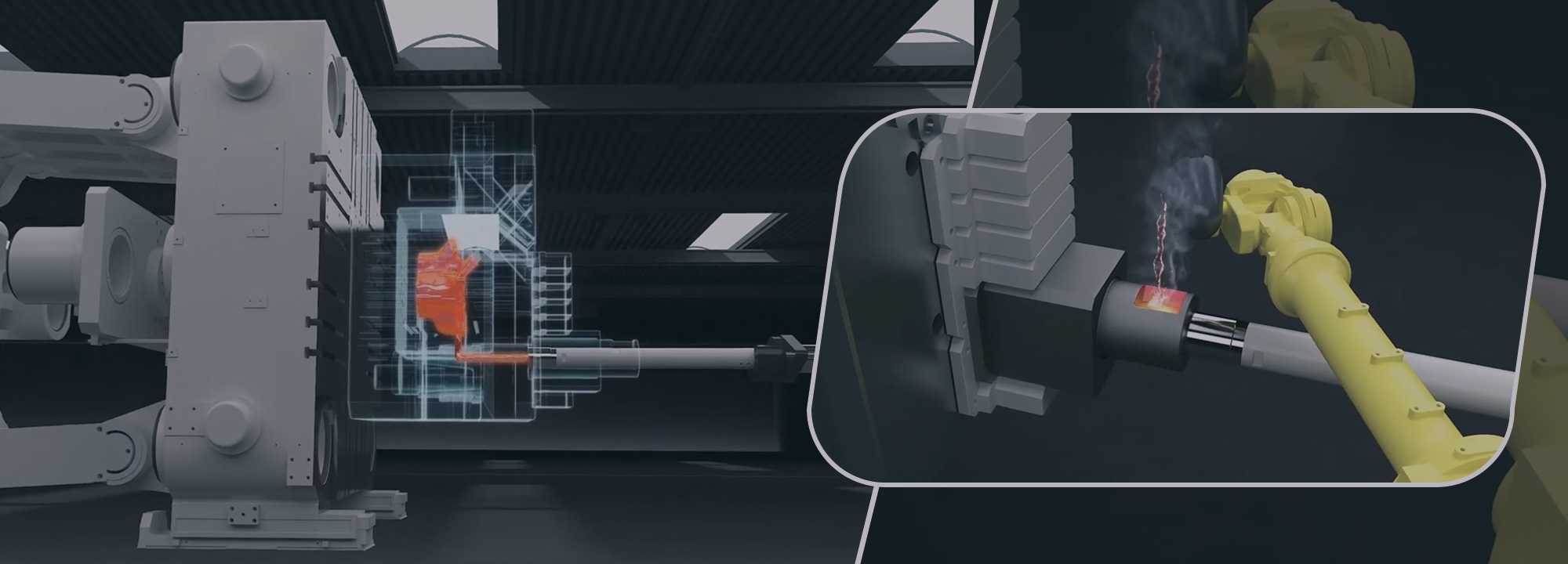
High-pressure die casting (HPDC) is a manufacturing process used to produce metal parts with high precision and efficiency. In HPDC, molten metal, typically aluminum or zinc alloys, is injected into a metal mold cavity at extremely high pressures, ranging from 1500 to 25,000 psi. This pressure ensures the metal fills the mold completely, creating intricate and detailed parts with excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy. HPDC is widely utilized in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics, for the production of complex components in large quantities.
High-pressure die casting commonly involves the sequential processes of mold preparation, injection, ejection, and post-casting treatment. While variations exist to meet specific product requirements, including vacuum die casting, slow-fill die casting, and semisolid metal processing (SSM), the general procedural steps are as follows:
High pressure casting process allows for the rapid injection of molten metal at high speeds, leading to significantly higher production rates compared to low-pressure or gravity casting methods.
High pressure die casting can obtain a thin wall thickness of under 0.40mm. The ability to produce thin walls not only contributes to weight reduction in the final products but also allows for the incorporation of inserts, commonly known as "co-cast" parts, such as screws and liners, during the casting process. This feature helps streamline assembly processes by reducing the overall number of components.
High pressure die casting (HPDC) offers the ability to create complex geometries in metal components. This capability makes HPDC well-suited for applications where complex designs and precise shapes are essential, such as in automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
HPDC ensures top-notch quality with precise dimensional accuracy, superior surface finish, and minimal trimming requirements. This process delivers uniformity, easing plating, and offers optimum mechanical properties, making it ideal for high-quality components.
High pressure die casting employs durable tools, known as dies, that withstand repeated use. This longevity reduces per-unit costs and makes HPDC economically efficient for large-scale production cycles.
HPDC is cost-effective for large-scale production due to its fast cycle times, high production rates, and reusable dies. These factors contribute to lower per-unit costs, making it an economical choice for mass manufacturing.
Choosing the right manufacturing process is crucial. At HuaYin, our team of experienced engineers offers expert advice and addresses queries in die casting services. With state-of-the-art facilities and efficient manufacturing plants, we ensure high-quality products. Benefit from fast lead times, quick online quotations, and free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis upon uploading your design file. Rest assured, we deliver excellence at competitive market prices.
01 What types of metals are commonly used in high-pressure die casting?
Magnesium, zinc, and aluminum are the most commonly used metals in high-pressure die casting due to their favorable properties such as lightweight, mechanical strength, and surface finish quality.
02 What Industries Commonly Use HPDC?
HPDC is commonly employed in industries such as automotive for manufacturing engine components and structural parts, aerospace for lightweight components, electronics for casings and connectors, and telecommunications for high-precision components.
03 Are the High-Pressure Casting Products Durable?
Yes, high-pressure casting products are highly durable, as the process can create parts with high strength and durability, even with wall thicknesses as thin as 1 mm.
04 How does the quality of parts produced by high-pressure casting?
High-pressure casting produces high-quality parts with finer tolerances (+/-0.1 mm) and better surface finishes (1.5 µm) compared to gravity casting. It also results in stronger and more durable components than other casting methods.
05 What Is High-Pressure Die Casting Used For?
High-pressure die casting is used for large production runs of metal components such as infusion pumps, airframes, jet engine thrust reversers, engine blocks, oil sumps, car crossbeams, gearbox casings, and engine mounts.
06 How Much Does High-Pressure Casting Cost?
High-pressure die casting has higher initial tooling costs, approximately $27,000 compared to $1,900 for sand casting. However, due to the longevity of high-pressure die casting tooling, which can last for up to 500,000 parts, the cost per part is much lower, around $0.05, compared to $0.38 per part for sand casting tooling, which may only last for 5,000 parts.